In Brief (TL;DR)
NFC is not just for payments: this versatile technology allows you to pair devices, read tags, and automate actions with a simple touch.
From pairing devices to automating daily actions, this wireless technology transforms the way we interact with the objects and environments around us.
From quick device pairing to automating daily tasks via NFC tags, the possibilities go far beyond the simple act of paying.
The devil is in the details. 👇 Keep reading to discover the critical steps and practical tips to avoid mistakes.
When you hear about NFC technology, you probably immediately think of contactless payments with your smartphone. You bring your phone close to the POS, a “beep,” and the purchase is done. Convenient, fast, and now part of our daily lives. But what if we told you that this little technological magic hides a universe of possibilities that go far beyond simple economic transactions? Near Field Communication, or NFC, is much more than a digital wallet: it is a key that opens the doors to a world of intelligent interactions, capable of uniting the physical and digital worlds in surprising ways.
From the walls of an ancient museum telling their story to your smartphone, to the home that adapts to your needs with a simple touch, NFC is silently revolutionizing our habits. In this article, we will explore together what this technology is really for, discovering practical applications that blend innovation and tradition, especially in the Italian and European context. Get ready to discover how such a simple gesture can activate complex experiences, making everyday life more efficient, interactive, and secure.

How NFC Technology Works in Brief
NFC (Near Field Communication) technology is a form of very short-range wireless communication. Think of two people exchanging a secret by whispering in each other’s ears: they must be very close for the communication to happen successfully and securely. Similarly, two devices equipped with NFC chips must be a few centimeters apart, usually less than 10, to exchange data. This proximity is its greatest strength, as it drastically reduces the risk of unwanted interceptions, making transactions secure. Unlike Bluetooth, NFC does not require a manual pairing process; the connection is almost instant, created by an electromagnetic field generated by one of the two devices.
Beyond the Register: A World of Possibilities
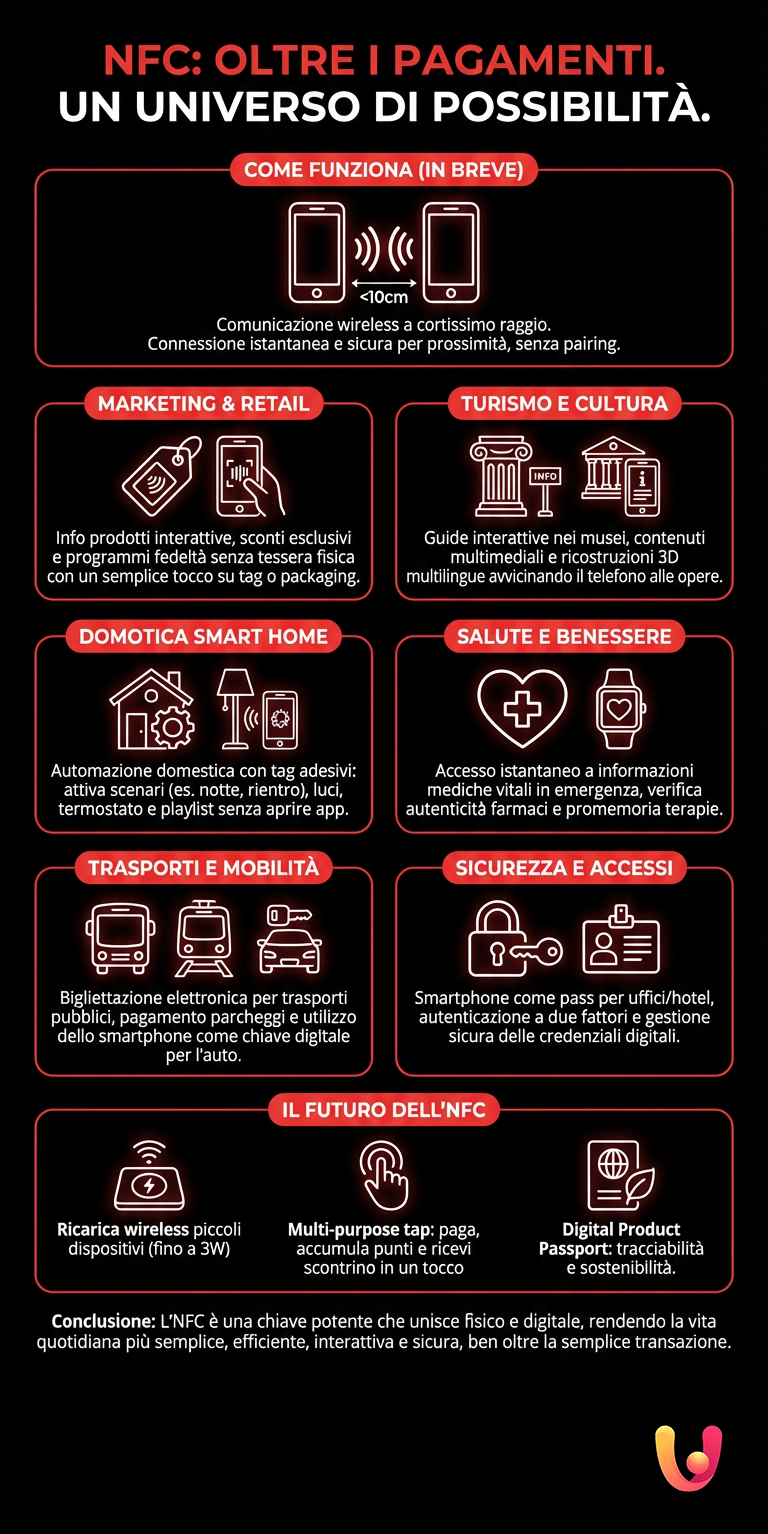
Although mobile payments are the most well-known use, the potential of NFC extends into many other sectors, transforming common objects into interactive tools. This versatile technology is finding application in marketing, tourism, home automation, and even healthcare, proving to be a powerful tool for innovation. Its ability to create a bridge between physical and digital opens scenarios where information and action are within “touch” reach, simplifying processes and enriching the user experience in ways previously unthinkable.
Marketing and Retail: An Interactive Shopping Experience
In the retail world, NFC is transforming the way we interact with products. Imagine being in a store and wanting to know more about a bottle of wine. By bringing your smartphone close to an NFC label (or “tag”) on the bottle, you could instantly access information about its origin, reviews, and recommended pairings. Brands use NFC tags on smart posters or packaging to offer exclusive content, discounts, or to participate in loyalty programs without the need for physical cards. This interaction not only enriches the shopping experience but provides retailers with valuable data on customer behavior, helping them optimize marketing strategies.
Tourism and Culture: Tradition Meets Innovation
In a country rich in history like Italy, NFC offers an innovative way to enhance cultural heritage. Museums and archaeological sites can use NFC tags to offer visitors interactive guides. By bringing the phone close to a tag near a work of art, one can receive detailed information, multimedia content, or 3D reconstructions directly on their device, even in multiple languages. This fusion of ancient and modern not only makes the visit more engaging and accessible but also allows for overcoming linguistic and physical barriers, such as the difficulty of installing information panels in delicate historical places. It is a perfect example of how technology can serve tradition, making it alive and speaking.
Home Automation and Smart Home: Simplicity at Your Fingertips
NFC is making the smart home even more intuitive. With simple NFC stickers, called tags, you can automate complex actions. For example, you could place a tag on the nightstand: by bringing your smartphone close before sleeping, the phone could activate “do not disturb” mode, turn off smart lights, and set the alarm. Another tag near the front door could activate your favorite playlist and adjust the thermostat when you return home. These small customizable “switches” eliminate the need to open multiple apps, making the management of home automation a natural and immediate gesture.
Health and Wellness: A Discreet and Powerful Aid
In the healthcare sector, NFC is proving to be a valuable tool for improving the efficiency and safety of care. Bracelets or cards equipped with NFC tags can contain a patient’s vital medical information, instantly accessible by a healthcare operator in case of emergency simply by bringing a device close. This technology can also be used to verify the authenticity of drugs, manage digital medical records, or send reminders for taking therapies. NFC offers a quick, secure, and low-energy way to manage sensitive data, reducing the risk of errors and optimizing care processes.
Transport and Mobility: Traveling with a Touch
NFC is also simplifying the way we move. Many public transport systems in Europe and Italy already use this technology for electronic ticketing. Travelers can purchase and validate tickets directly with their smartphones, eliminating queues and the need for paper tickets. In addition to public transport, NFC finds application in parking payments and even as a digital key for the car. Its speed and simplicity of use make every movement smoother and more integrated, contributing to creating smarter and more connected cities. For optimal management of smartphone connectivity, NFC represents a fundamental piece.
Security and Access Control: Digital Keys and Secure Identity
Thanks to its short-range nature, NFC is an ideal technology for access control. Instead of a physical key or badge, the smartphone can become your pass to enter the office, a hotel, or an event. This not only increases convenience but also security: digital credentials can be managed and revoked remotely in real-time. NFC can also be used for two-factor authentication, adding a layer of protection for access to corporate networks and data. The use of the smartphone as a secure identity tool is one of the most promising frontiers, ensuring that only authorized persons can access sensitive places and information, a crucial aspect for a secure smartphone.
The Future of NFC in Italy and Europe

The future of NFC technology appears bright and full of developments. The NFC Forum, the association that promotes its standard, is working to increase the range and power of the technology, for example by bringing wireless charging capacity from 1 to 3 watts. This could enable the charging of small devices like earbuds or smartwatches simply by resting them on another device. Another key innovation is the “multi-purpose tap,” which will allow performing multiple actions with a single touch: paying, accumulating loyalty points, and receiving the digital receipt simultaneously. In Europe, these evolutions integrate with initiatives like the Digital Product Passport, which will use NFC to provide detailed information on the sustainability and traceability of products, in line with the transparency goals of the single market.
Conclusions

In conclusion, NFC technology is much more than a simple tool for contactless payments. As we have seen, its applications extend to almost every aspect of our daily life, making it simpler, efficient, and interactive. From enriching a museum visit to managing the smart home, from making medical care safer to smoothing transport, NFC confirms itself as a discreet but very powerful technology. In the Italian and European context, its ability to combine innovation and tradition makes it particularly valuable. Looking to the future, with the increase in its capabilities and integration into new regulations, NFC is destined to become an even more central tool in our interaction with the digital and physical world, demonstrating that the greatest revolutions, sometimes, begin with the simplest of gestures: a touch.
Frequently Asked Questions

What exactly is NFC technology?
NFC stands for Near Field Communication. It is a short-range wireless transmission technology that allows two devices to exchange data when they are at a very close distance, usually less than 10 centimeters. It works through electromagnetic induction between two antennas. Unlike other technologies like Bluetooth, NFC does not require a manual pairing process, and the connection is almost instant, making it ideal for quick and secure interactions. Its short range is an advantage in terms of security, as it minimizes the risk of data being intercepted by third parties.
What are the most common uses of NFC besides payments?
Besides payments, NFC has a wide range of practical applications. It is used for access control, transforming the smartphone into a digital key for doors, offices, or events. In the transport sector, it enables electronic ticketing on buses and subways. In home automation, NFC tags can be programmed to automate actions like turning on lights or setting the alarm. In marketing, it allows access to product information or special offers via “smart posters.” Finally, it is crucial in tourism for interactive guides in museums and in healthcare for quickly accessing a patient’s medical information.
Does my smartphone have NFC? How can I activate it?
Most modern smartphones are equipped with an NFC chip. To check if your Android device supports it, you can swipe down the quick settings menu (the one that appears by dragging your finger from the top of the screen) and look for the NFC icon. Alternatively, you can go to Settings, search for “NFC” or check in the sections related to “Connections” or “Connected devices.” If you find the option, make sure the switch is on. On iPhones (from model 6 onwards), NFC is present and always active for functions like Apple Pay, but use for reading tags is generally automatic and does not require manual activation by the user.
Are NFC tags secure? Can they be hacked?
Security is one of NFC’s strengths, mainly thanks to its reduced operating distance. Since devices must be a few centimeters apart, it is very difficult for a malicious actor to intercept the communication without being physically obvious. Furthermore, transmitted data, especially for sensitive applications like payments or access control, use advanced encryption systems (such as tokenization) that protect the original information. Although no system is 100% infallible, the intrinsic characteristics of NFC and the implemented security protocols make it a very reliable technology for most daily uses.
What are NFC tags and how are they used?
NFC tags are small passive chips, often in the form of stickers or cards, that do not need their own power source. They contain a small amount of memory that can be programmed with specific information, such as a link to a website, Wi-Fi network data, a contact, or a command for an app. To use them, simply bring a smartphone with active NFC close to the tag. The phone reads the information and performs the programmed action. For example, you can program a tag with a specific app to start your favorite playlist when you touch it, or to share the Wi-Fi password with guests without having to type it. They are a versatile and affordable tool for creating personalized automations and shortcuts.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, NFC technology is generally considered secure even for uses not related to payments. Its fundamental characteristic is very short-range communication, which usually does not exceed 10 centimeters, but often hovers around 3-4 cm. This drastically reduces the risk of unauthorized interceptions. Furthermore, data on NFC tags can be encrypted, and the tags themselves can be locked to prevent unauthorized modifications. For more delicate operations, such as access to restricted areas or starting home automations, security is further strengthened by apps that require authentication (such as PIN or biometrics) on the smartphone before executing the command.
NFC tags are small passive electronic chips, often in the form of stickers or inserted into objects like keychains and cards, which do not require batteries. By bringing a smartphone close, the tag activates and transmits a small amount of information. Everyday uses are plentiful: you can apply a tag near the front door to activate/deactivate Wi-Fi and lights with a touch, use it in the car to start the navigator and your favorite playlist, or create a digital business card that instantly shares your contacts. They are also used in museums to provide information on works of art or on products in stores.
No, not all smartphones are equipped with NFC, although most mid-range and high-end models produced in recent years include it. To check if your Android smartphone has NFC, go to «Settings», look for the «Connected devices» or «Connections» section, and check if the «NFC» option is present. If it is there, you can activate it from there. regarding iPhones, all models starting from the iPhone 7 are equipped with an NFC chip. On newer iPhones (from the XR model onwards), NFC is always active in the background for reading tags, while for payments it must be configured via the Wallet app.
Absolutely yes. In the healthcare sector, NFC technology is used to improve efficiency and safety. For example, bracelets or cards with NFC tags can contain a patient’s medical record, allowing medical staff to quickly access vital information such as allergies or ongoing therapies. This speeds up interventions, especially in emergency situations. For event access, NFC is an excellent alternative to paper tickets or QR codes. You can buy a ticket online and load it onto your smartphone; to enter a concert, a museum, or public transport, just bring the phone close to the reader at the entrance.
An NFC business card is a physical card, often made of PVC or wood, containing a small NFC chip. When a person brings their smartphone (with active NFC) close to the card, a notification appears on the phone that directly opens a web page with all your information: contacts, links to social media, website, portfolio, and much more. The main advantages are innovation and practicality: there is no need to manually transcribe data, the impact is memorable, and information can be updated at any time without having to reprint the card. It is also an eco-friendly choice because a single card can be used indefinitely, reducing paper waste.



Did you find this article helpful? Is there another topic you'd like to see me cover?
Write it in the comments below! I take inspiration directly from your suggestions.