In everyday life, the choice between using a Wi-Fi network or mobile data has become an almost automatic decision, an instinctive gesture we perform multiple times a day with our smartphones. Yet, behind this choice lies a strategic balance between speed, costs, security, and battery life. In an increasingly connected Italy, where the tradition of a solid home network blends with the innovation of constant connectivity, understanding when and why to prefer one technology over the other is not just a matter of Gigabytes, but a way to optimize our digital lives.
Let’s imagine the Wi-Fi connection as the domestic hearth: a stable, reliable, and generous point of reference. Mobile data, on the other hand, represents the freedom to explore, the possibility of staying connected everywhere, from the town square to a high-speed train. Both solutions are indispensable, but knowing their strengths and weaknesses allows us to make the most of them, turning a simple habit into a conscious and intelligent choice.
Wi-Fi and Mobile Data: Two Sides of the Same Coin
Wi-Fi is a technology that allows devices to connect to the Internet wirelessly, using radio waves transmitted by a router connected to a fixed broadband line. It is the ideal solution for indoor environments such as homes, offices, cafes, and libraries, where it can support multiple devices simultaneously. Its nature is stationary, tied to a physical location, representing stability and an abundance of resources, typically with flat rate plans that do not impose traffic limits. This characteristic makes it a pillar of modern family and work life, much like electricity or running water.
Mobile data, conversely, offers connectivity through the network of cellular operators (4G, 5G). Its strength lies in mobility: it is available wherever there is network coverage, keeping us connected while on the move. This technology embodies innovation and flexibility, adapting to a dynamic lifestyle. However, the data connection is tied to rate plans with a monthly Gigabyte threshold, and its performance can vary depending on signal quality. Understanding this duality is the first step toward efficient management of one’s connectivity.
Speed Comparison: Who Wins the Race?
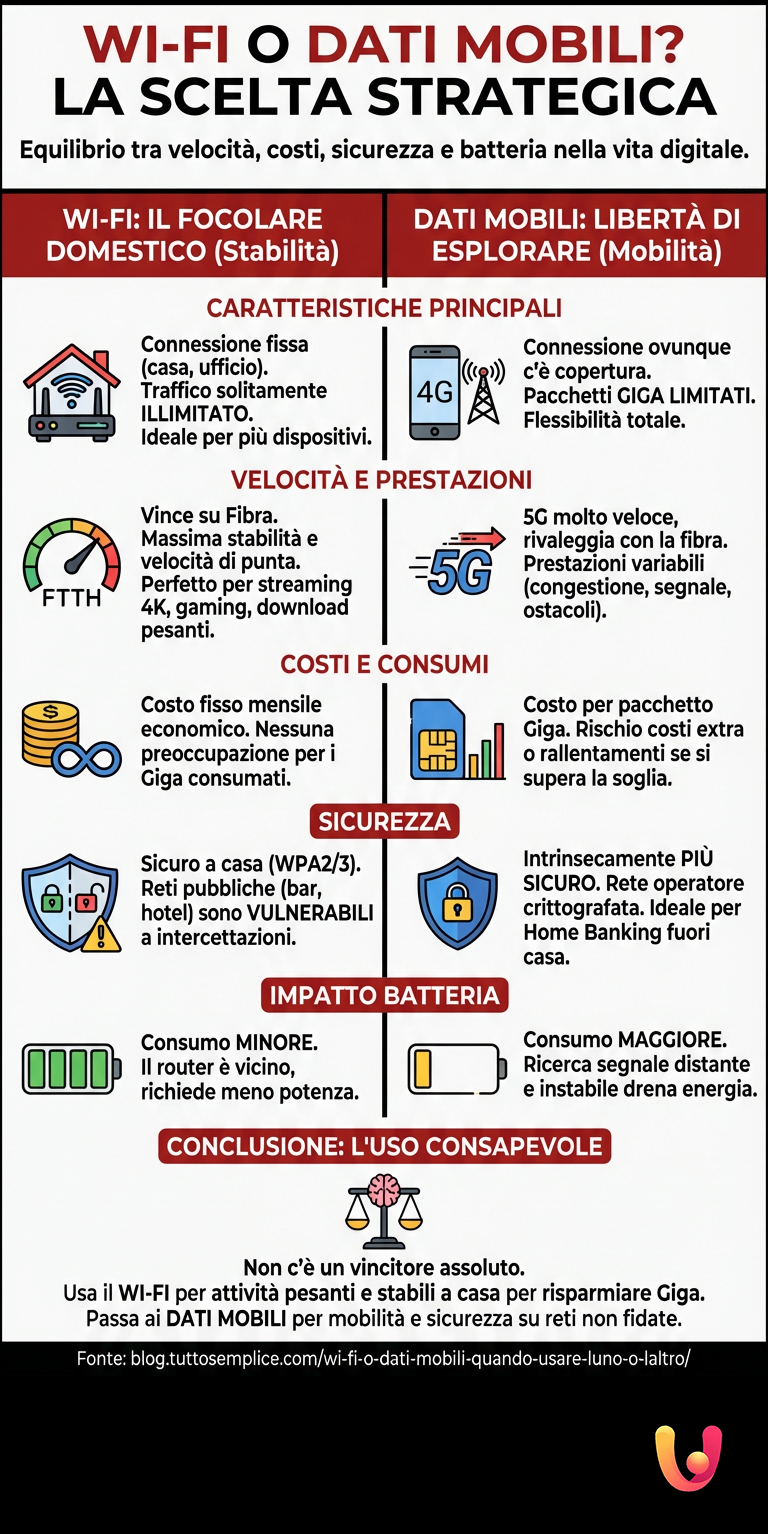
In terms of pure speed, the comparison is not always obvious. A fiber-optic based Wi-Fi connection (FTTH) offers, in most cases, superior and more consistent performance compared to the mobile network, with speeds that can reach and exceed 1 Gigabit per second (Gbps). This makes it the undisputed choice for bandwidth-intensive activities, such as streaming 4K content, competitive online gaming, or downloading large files. The stability of the Wi-Fi signal within the home or office is another crucial advantage, ensuring a smooth and uninterrupted experience.
On the other hand, the advent of 5G in Italy has shuffled the deck. In areas with excellent coverage, the 5G network can reach speeds comparable to those of good fiber, clearly surpassing 4G and many non-fiber Wi-Fi connections. However, mobile data speed is more subject to variables such as network congestion, distance from the operator’s cell tower, and the presence of physical obstacles. Therefore, while fiber Wi-Fi wins for stability and peak speed at a fixed point, 5G offers impressive speed on the go, bridging a gap that seemed unbridgeable just a few years ago.
Costs and Data Consumption: Your Wallet Will Thank You

From an economic standpoint, the difference is substantial. Home or business Wi-Fi connections are almost always based on monthly fixed-cost subscriptions, which offer unlimited data traffic. This model is extremely advantageous for those with high consumption, allowing users to browse, download, and stream content without the worry of running out of Gigabytes. In Italy, the average cost for a fixed connection is around 26 euros. This predictability of expense makes Wi-Fi the backbone of connectivity for families and professionals.
Mobile data, instead, is generally sold in packages with a defined amount of Gigabytes. Although offers have become increasingly generous, exceeding the threshold can result in additional costs or a drastic reduction in browsing speed. It is interesting to note that Italy is one of the cheapest countries in Europe for mobile data costs, a factor that has driven its mass adoption. The strategic choice, therefore, is to reserve the “heaviest” activities for the Wi-Fi network, preserving precious mobile Gigabytes for when you are away from home.
When to Choose Wi-Fi: Stability and Savings
Choosing Wi-Fi is the most logical and advantageous option in a series of well-defined contexts. First of all, at home and in the office, where the network is stable, secure, and without consumption limits. It is the ideal option for smart working, remote learning, and home entertainment. Using Wi-Fi for these activities not only guarantees better performance but also completely frees up mobile data for when it is truly needed.
Secondly, Wi-Fi is indispensable for all operations requiring large data transfers. Think of operating system updates for smartphones or computers, downloading heavy applications or video games, and especially performing a smartphone backup to the cloud. Entrusting these operations to mobile data could erode a large part of your data plan in just a few minutes. Finally, for high-resolution video streaming (4K) and online gaming, the low latency and high bandwidth of a good Wi-Fi connection are essential for a lag-free and buffer-free experience.
When to Rely on Mobile Data: Freedom and Flexibility
Mobile data becomes our best ally when the keyword is movement. On public transport, during a walk in the city, or while traveling, the cellular network ensures we stay connected to check maps, stream music, or communicate via messaging apps. The capillarity of the 4G network, and increasingly 5G, ensures extensive coverage over most of the national territory, offering priceless freedom.
Another key scenario is when you are in places with absent, slow, or unreliable public Wi-Fi. In these situations, switching to mobile data is often the quickest and most stable solution. Furthermore, your operator’s data connection is intrinsically more secure than an unprotected public Wi-Fi network. When you need to perform sensitive operations, such as accessing your online banking or entering credentials, and you do not have a trusted Wi-Fi network available, using mobile data is a wise precaution to protect your privacy. For even greater security on public networks, it is advisable to consider the use of a VPN (Virtual Private Network).
Security: A Factor Not to Be Underestimated
Security is a critical aspect that is often overlooked. Home or business Wi-Fi networks, if protected by a strong password and WPA2 or WPA3 encryption, are generally secure. The real risk arises with public Wi-Fi networks, such as those in airports, hotels, or cafes. These networks are often unencrypted, leaving transmitted data vulnerable to interception by malicious actors connected to the same network (“man-in-the-middle” attacks). A hacker could create a fake hotspot with a credible name to induce users to connect and thus steal sensitive information.
Mobile data connection, however, offers an intrinsically higher level of security. Data travels on the telephone operator’s network, which uses advanced encryption protocols, making it much more difficult for an outsider to intercept the communication. For this reason, it is good practice to avoid performing delicate activities like bank transactions, online purchases, or sending confidential documents when connected to a public Wi-Fi network. In these cases, it is always preferable to switch to the safer data network of your smartphone.
Impact on Battery: A Detail That Makes the Difference
Smartphone battery life is also influenced by the choice of connection. Generally speaking, all things being equal, Wi-Fi consumes less battery compared to 3G/4G/5G data connections. The reason is related to transmission power: the Wi-Fi router is a nearby device, usually a few meters away, and the smartphone requires little energy to communicate with it. Conversely, connecting to the mobile network requires reaching an antenna (the base station) that can be hundreds of meters or even kilometers away, requiring greater energy expenditure.
Signal quality is a determining factor. A smartphone constantly trying to lock onto a weak cellular signal will consume a lot of energy. Therefore, in areas with poor mobile coverage, keeping the network search active can drain the battery quickly. In these contexts, if a stable Wi-Fi network is available, using it will not only improve the connection but also have a positive impact on battery. Turning off Wi-Fi when you are on the move and there are no known networks to connect to can, in turn, contribute to small energy savings.
The Italian Context: Tradition and Innovation Online
In Italy, the choice between Wi-Fi and mobile data reflects an interesting blend of tradition and innovation. The home, the hub of Mediterranean culture, has become the digital hub par excellence, where a powerful and unlimited Wi-Fi connection is now considered a primary good. It supports children’s studies, parents’ remote work, and evening entertainment for the whole family. In parallel, Italy has enthusiastically embraced the mobile revolution. According to data from May 2024, 94.5% of the Italian population between 18 and 74 years old browsed via mobile, generating almost 90% of the total time spent online.
This massive adoption has been favored by some of the most competitive mobile data offers in Europe, transforming every square, every bar, and every means of transport into a potential office or cinema hall. Projects like “Piazza WiFi Italia” aim to further extend free connectivity throughout the territory, even if diffusion is not yet widespread. The Italian user therefore moves with agility between these two worlds: the solid and traditional fortress of domestic Wi-Fi and the innovative and flexible freedom of mobile data, demonstrating a digital maturity that wisely balances the two technologies.
In Brief (TL;DR)
Discover when it is better to use Wi-Fi versus mobile data to optimize speed, data consumption, and battery life.
Learn how to make the right choice in every situation to browse faster, save data, and extend your device’s battery life.
We analyze the key factors to decide when it is better to use Wi-Fi or mobile data, so as to optimize speed, data consumption, and battery life.
Conclusions

In conclusion, there is no absolute winner in the challenge between Wi-Fi and mobile data. The best choice is never “either one or the other,” but a strategic and combined use of both technologies. Wi-Fi reigns supreme in stable environments like home and office, offering speed, reliability, and unlimited traffic, ideal for data-intensive activities and for saving battery. Mobile data, on the other hand, is the symbol of freedom and flexibility, ensuring connectivity everywhere and offering a higher level of security compared to public Wi-Fi networks.
The conscious user knows that the secret lies in balance. They rely on Wi-Fi for heavy downloads, high-quality streaming, and long work sessions, preserving the Gigabytes of their mobile plan. When on the move or when security is a priority, they switch agilely to the data network. Mastering this simple alternation means optimizing costs, maximizing performance, and protecting one’s privacy, transforming the smartphone into an even more powerful and efficient tool in our daily lives.
Frequently Asked Questions

Generally, yes. Wi-Fi connection tends to consume less battery compared to mobile data. This happens because the Wi-Fi signal comes from a nearby router, requiring less energy for transmission. Conversely, the data connection must reach a telephone operator antenna, which can be much further away, forcing the smartphone to expend more energy, especially if the signal is weak.
Your operator’s data connection is intrinsically more secure than a public Wi-Fi network. Mobile data travels on an encrypted and private network between your device and the operator. Public Wi-Fi networks, on the other hand, can be exploited by malicious actors to intercept information you exchange online. For this reason, it is always advisable to use the data connection for sensitive operations, such as online banking, when you are away from home.
For streaming heavy content like movies, TV series, or music, Wi-Fi is almost always the best choice. It offers a generally more stable and faster connection, avoiding interruptions and buffering. Furthermore, using Wi-Fi does not consume the Gigabytes of your data plan, which would run out very quickly with high-definition video streaming. Many apps, such as Netflix or Spotify, also allow you to download content via Wi-Fi to watch or listen to it offline later.
Although Wi-Fi is often perceived as faster, there are situations where mobile data, especially with 5G technology, performs better. This can happen if the Wi-Fi network you are connected to is very crowded, if the router signal is weak, or if the home internet connection is slow. In these contexts, switching to a 4G or 5G network with a good signal can guarantee decidedly smoother and faster browsing.
To avoid running out of Gigabytes, you can adopt some simple measures. From your smartphone settings, on both Android and iPhone, you can monitor which apps consume the most data and set a usage limit or a data saver mode. It is also useful to disable automatic download of photos and videos on apps like WhatsApp and automatic app updates, reserving these operations for when you are connected to Wi-Fi.
Still have doubts about Wi-Fi or Mobile Data? When to Use One or the Other?
Type your specific question here to instantly find the official reply from Google.







Did you find this article helpful? Is there another topic you’d like to see me cover?
Write it in the comments below! I take inspiration directly from your suggestions.