Imagine paying for your coffee at a café, your subway ticket, or groceries at the supermarket with a simple wave of your hand, without having to search for your smartphone or wallet. It isn’t science fiction, but the increasingly concrete reality of wearable payments. Beyond smartwatches, which have already accustomed many to this convenience, the new frontier is represented by rings and bracelets equipped with NFC technology. These devices transform a fashion accessory into a practical payment tool, combining style, security, and unprecedented immediacy. This evolution marks a decisive step toward a future where technology integrates invisibly and naturally into our daily lives.
The rise of these new tools fits into a context of strong growth for digital payments. In Italy, in 2024, innovative payments via smartphones and wearable devices reached 56.7 billion euros, an increase of 53% compared to the previous year. This data, provided by the Innovative Payments Observatory of the Polytechnic University of Milan, highlights how Italians are increasingly inclined to adopt solutions offering speed and practicality, progressively abandoning cash. NFC rings and bracelets represent the ultimate expression of this trend, promising to make the act of payment even more fluid and secure.
What Wearable Payments Are and How They Work
Wearable payments are transactions made via accessories or clothing items equipped with wireless communication technologies. The heart of these devices is the NFC (Near Field Communication) chip, a technology that allows two devices to exchange data securely when they are a few centimeters apart. Unlike smartwatches, payment rings and bracelets are often “passive”, meaning they do not require a battery to function. The integrated NFC chip is powered directly by the electromagnetic field of the POS terminal at the moment of the transaction, making them always ready for use. To learn more about how this technology works, you can consult our guide on the magic of contactless payments.
The process is very simple. The user connects their wearable device to a debit, credit, or prepaid card via a dedicated app. During this phase, sensitive card data is replaced by a “token”, a unique digital code that ensures maximum security. When you want to make a payment, simply bring the ring or bracelet close to the enabled POS reader. The transaction takes place in a few moments, just like with a normal contactless card. For amounts above the standard threshold (usually 50 euros), entering the PIN of the associated card may be required, adding an extra layer of protection.
The Wearable Market in Italy and Europe
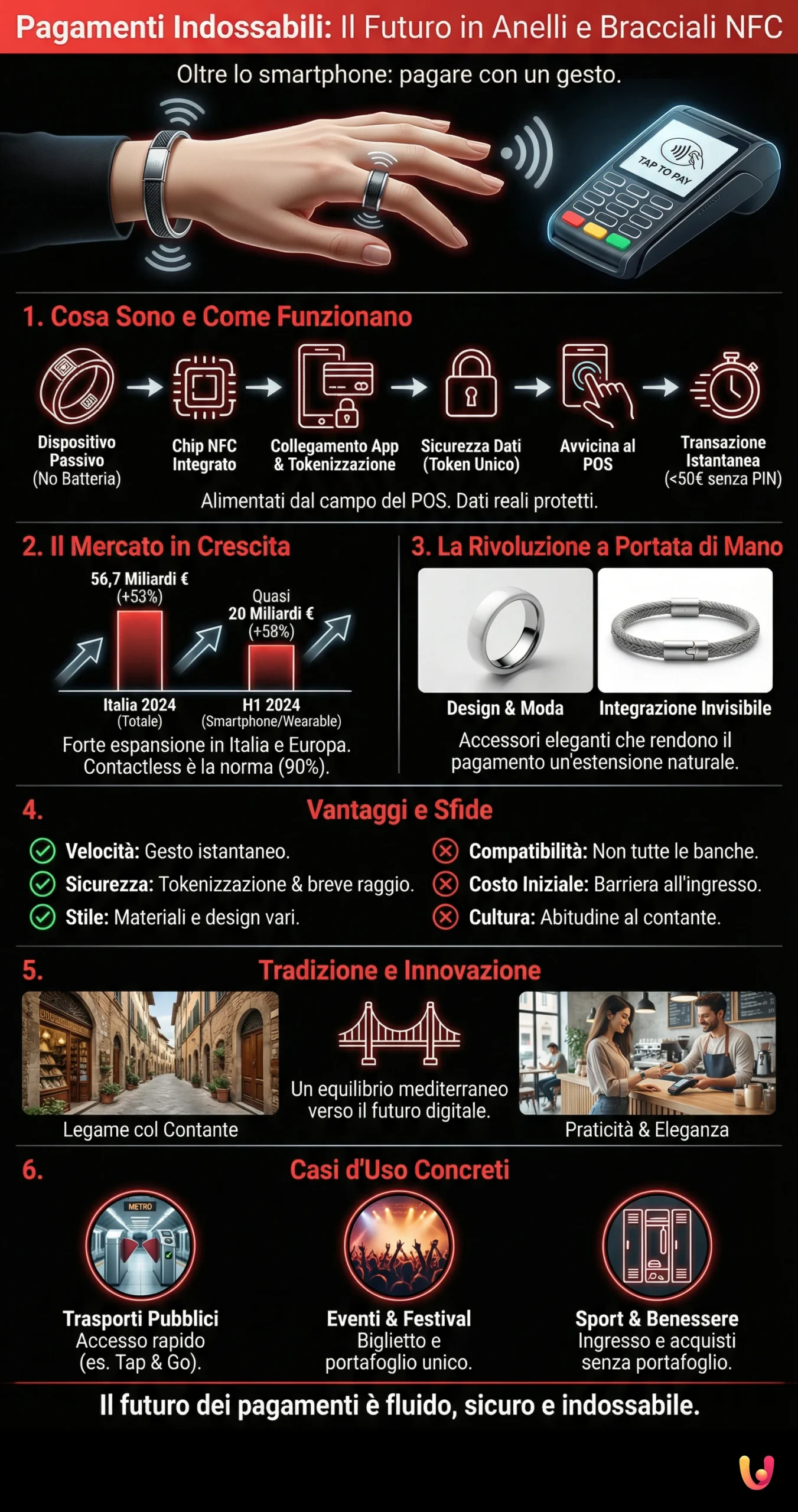
The wearable payments market is experiencing a phase of strong expansion both in Italy and the rest of Europe. Growing familiarity with contactless payments, which now represent almost 90% of electronic in-store transactions in our country, has paved the way for these new technologies. According to recent studies, one in four European consumers is already inclined to use wearable devices for their purchases. Italy aligns with this average, showing significant openness towards innovation, despite a cultural tradition still linked to cash. Growth is driven by the perception of simplicity and speed that these tools offer.
Statistics confirm this positive trend. In the first six months of 2024, payments via smartphones and wearables in Italy recorded a 58% increase in transaction value, reaching nearly 20 billion euros. Although Italy still lags behind other European countries in the number of digital transactions per capita, annual growth is among the highest on the continent. This scenario suggests enormous potential for NFC rings and bracelets, which appeal to an increasingly vast audience, from Generation Z digital natives to more mature consumers who appreciate their convenience.
NFC Rings and Bracelets: The Revolution at Your Fingertips

Rings and bracelets represent the most discreet and integrated evolution of digital payments. These accessories transform a daily gesture into a fluid experience, eliminating all friction. It is no longer about searching for a card in a wallet or unlocking an application on a smartphone: payment becomes a natural extension of one’s body. The goal is to make the transaction almost “invisible”, focusing attention on the shopping experience rather than the act of paying. This revolution combines cutting-edge technology and design, making devices not only functional but also true fashion accessories.
The Advantages: Speed, Security, and Style
The benefits offered by NFC rings and bracelets are manifold. The first and most obvious is speed: paying becomes an instant gesture. This proves particularly useful in dynamic contexts like public transport or during a crowded event. Security is another strong point. Thanks to tokenization technology, real card data is never shared with the merchant, drastically reducing the risk of fraud. Furthermore, NFC communication works only at a very close range, making interception almost impossible. For more details on protection, it is useful to read the article explaining if contactless payment data is really safe. Finally, style: these devices are available in various materials and designs, from ceramic to steel, transforming from simple tech gadgets into personal and elegant accessories.
Disadvantages and Challenges to Overcome
Despite the numerous advantages, large-scale adoption of wearable payments still has to overcome some challenges. One of the main obstacles is compatibility: not all banks and payment circuits support these devices yet, although aggregator platforms like Curve are expanding possibilities. Another aspect to consider is the initial cost of the accessory, which may represent a barrier for some users. Finally, there is a cultural component linked to habit and a certain wariness towards technologies perceived as too new. In case of loss, it is essential to be able to block the device quickly via the dedicated app, a procedure that users must learn to know.
Tradition and Innovation: A Mediterranean Balance
In a country like Italy, where traditions carry significant cultural weight, the introduction of new payment technologies represents a fascinating challenge. Mediterranean culture is often associated with a strong bond with cash, seen as a tangible and familiar tool. However, the same culture values sociality, practicality, and elegance, elements that wearable payments manage to interpret in a modern key. A ring or bracelet, unlike a complex app, maintains a physicality, uniting the digital world with an object one can touch and wear. This can favor its acceptance even by those less accustomed to technology.
The balance between tradition and innovation is the key to success. NFC wearables do not seek to completely replace established habits, but to offer a simpler and safer alternative. Let’s imagine a small merchant in a historic village accepting a payment from a tourist via a ring: it is an image that blends the past with the future. Technology thus becomes a bridge, a way to make daily interactions more efficient without losing human contact. The growing adoption of digital payments in Italy demonstrates a strong desire for innovation, and wearable devices are ready to satisfy it discreetly and elegantly.
Concrete Use Cases: Beyond Just Coffee
The applications of NFC rings and bracelets go far beyond simply paying for coffee. One of the most promising sectors is public transport. In many cities, it is already possible to pay for the ride directly at the turnstile with contactless cards; wearables make this operation even faster, eliminating the need to take out tickets or passes. An example is Rome’s Tap & Go system, which enables access to public transport via cards and NFC devices. For travelers, saying goodbye to the paper ticket becomes a convenient and immediate reality.
Another area of great interest is that of events, such as concerts, festivals, and fairs. NFC bracelets can serve as both an entry ticket and a digital wallet, allowing the purchase of food, drinks, and merchandise with a simple touch. This not only reduces queues and improves the attendee experience but also increases security by eliminating the need to carry large amounts of cash. Finally, let’s think about the world of sports and wellness: paying for entry to the gym or pool, or a drink at the sports club bar, without having to carry a wallet into the locker room, is a priceless convenience that these devices make possible.
In Brief (TL;DR)
Wearable payments, through rings and bracelets with NFC technology, are defining the new frontier of digital transactions, making every purchase more immediate, secure, and integrated into our daily lives.
From smart rings to elegant bracelets, let’s discover how these accessories are redefining the concept of the digital wallet.
This innovation is destined to redefine the shopping experience, making every transaction faster, safer, and perfectly integrated into our lifestyle.
Conclusions

Wearable payments, embodied by NFC rings and bracelets, are not a passing fad, but a fundamental stage in the evolution of digital payments. They represent the perfect synthesis of functionality, security, and style, integrating technology into our lives almost imperceptibly. Although challenges related to compatibility and diffusion still exist, the trajectory is clear: the market is growing strongly, and consumers, especially in Italy and Europe, are proving increasingly open to solutions that simplify daily life. Their ability to unite the physical world with the digital one makes them an incredibly versatile tool, ready to conquer not only digital natives but anyone looking for practicality without compromise. The future of payments is at hand, or rather, on the finger or wrist.
Frequently Asked Questions

These wearable devices contain a small passive NFC (Near Field Communication) chip, connected to a payment card or digital wallet. The ring or bracelet does not have an internal battery; it is powered for a few moments by the magnetic field of the payment terminal (POS) when brought close to pay. In practice, it works like a normal contactless card: simply bring your hand close to the reader to complete the transaction quickly and securely.
Yes, security is comparable to that of contactless credit cards and smartphone payments. Transactions use «tokenization», a process that replaces sensitive card data with a unique and encrypted code for each purchase. Furthermore, NFC technology works only at a very close range (less than 4 centimeters), making remote interception almost impossible. For amounts above a certain threshold (generally 50 euros), entering the PIN on the POS is still required, adding an extra layer of protection.
In case of theft or loss, it is essential to act promptly. You can immediately block the device via the provider’s mobile application, making it unusable for payments. The operation is similar to blocking a lost credit card. Once blocked, you can contact customer service to evaluate replacement options, ensuring maximum protection of your funds.
No, one of the main advantages of payment rings and bracelets is that they do not require any charging. Being «passive» devices, they do not have a battery. The NFC chip inside activates and is powered exclusively by the radio signal emitted by the POS terminal at the moment of payment. This ensures that your accessory is always ready for use, 24 hours a day, without having to worry about battery life.
Absolutely yes. Payment rings and bracelets work on international circuits like Visa and Mastercard. This means you can use them to pay in any shop, restaurant, or service in the world that has a payment terminal (POS) enabled for contactless. They work exactly like an international credit or debit card, offering great convenience during travels.
Still have doubts about Wearable Payments: The Future in NFC Rings and Bracelets?
Type your specific question here to instantly find the official reply from Google.







Did you find this article helpful? Is there another topic you’d like to see me cover?
Write it in the comments below! I take inspiration directly from your suggestions.